Computer Networks: Types, Topologies, and Benefits
A computer network is a system that connects two or more computers together using a communication link.
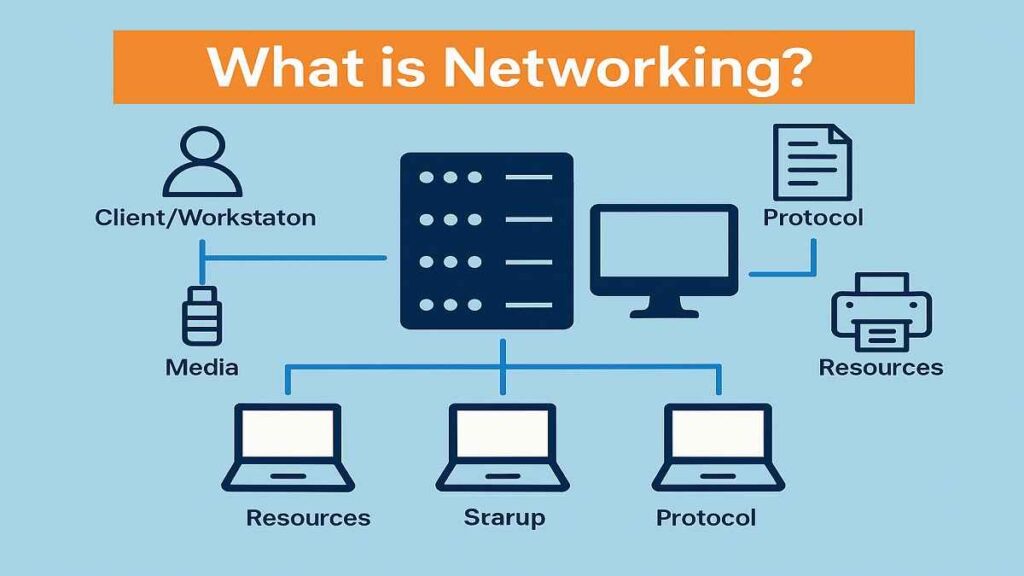
It describes a processing system with some independent, relatively low-speed, online, simultaneously usable workstations. In a network, remotely located computer stations are connected to a centrally located sophisticated, high-speed processor via a communication link (telephone lines, microwave links, satellite) for the purpose of sharing resources like printers, processor, programs, and some other information.
Work station/ Client: Each computer in a network is often referred to a work station or clients. Clients are the computers that can access the shared network resources provided by a server.
Server: A server provides shared resources and data over a network. It is usually a high-performance micro-computer with several drives often given several gigabytes of capacity and perhaps a few CD-ROM drivers, Servers allow all the microcomputers to have access to an external network via the network communication system.
Media: The computers are linked to each other by hardware components such as cables (UTP, STP, coaxial and fiber optics)
User: This is any person that uses a client to access resources on the network.
Resources: These are files, printers, modem or other items that can be used by network users. These
can be hardware or software resources.
Protocol: They are written rules used for communication. They are language that computers used to talk to each other over a network eg. TCP/IP, AppleTalk
Categories of Computer Networks
Computer networks are categorized according to how they are organized, the way in which they are used, and the limit of distance covered in the area of operation. These include:
- Local Area Network (LAN).
- Wide Area Network ( WAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
LOCAL AREA NETWORK
This is a popular form of network which refers to the connection of computers within a limited geographical area or within the same building or different building on the same site. Several LANs can be connected by the use of bridges and routers.
WIDE AREA NETWORK
This is a network between large geographical area. It is a global connection of computers. They are more sophisticated and use superior transmissions channel like microwave and satellite transmission to reach users over very long distance.
One of the most widely used of WANs is the Internet, which allows users to connect to other user worldwide.
METROPOLITAN AREA NETWORK
This is a network used to link users within metropolis or city.
Network Topology
Topology is the term used to describe the physical arrangement of computer in networks. A computer network can be arranged or configured in several different ways:
Types of network Topology
- Star Topology
- Bus Topology
- Ring Topology
- Hierarchical Topology
1. Star Network:
In a star network, a number of small computers are connected to the central resources usually called a host computer or file server. The star is a common arrangement for linking several microcomputers to a mainframe and providing a tine sharing system.
This arrangement provides high security because every communication between workstations must be via the central node computer (servers)
Advantages of star Topology
- It is most reliable because if a node or a node cable fails it does not affect the other nodes.
- New nodes or devices can easily be connected without affecting rest of the network.
- Performance of the network is dependent on the capacity of the central hub, adding further nodes do not greatly affect the overall performance.
- Existence of centralized management helps in monitoring the network.
- Ease of installation and upgrading from a hub to a switch.
- Simple and cheap.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
- If the server or the link to the server fails, the whole network is bound to fail.
- The additional devices such as hubs or switch increase the overall cost.
- The addition of more nodes depends on the capacity of the central device.
- Reconfiguration, fault isolation and installation of new devices tend to be difficult.
2. Bus Topology:
It has a common cable to which all the computers on the network are linked. The common cable is usually terminated at each end. One or more of the stations on the network acts as the file server. An example of the bus system is the ETHERNET.
Advantages of Bus Network
- Installation is very simple and cheap.
- It is suitable for temporary network.
- The failure of one node does not affect the rest of the bus network.
- Flexibility of nodes is visible as they can be attached or detached without any problem.
- Troubleshoot is easier compared with ring topology.
3. Ring Network:
It uses one network cable to connect all the workstation in an arrangement that looks like a ring. Ring networks are less secure because data intended for a particular machine may have to pass by other machines before it gets to its destination in the network.
Advantages of Ring Network
- This is an orderly network, where every device has access to token and the privilege to transmit and this helps to reduce chances of collisions.
- Equal access to resource by each computer or node.
- The performance of the network is not affected by additional components
- Installation and reconfigure is made easy since addition or deletion of a device requires moving just two components.
- No need of central server to manage the connectivity between the computers or nodes.
Disadvantages of Ring Network
- The hardest of all topology to troubleshoot because it can be hard to track down where in the ring, the failure has occurred.
- Addition, changing and moving the nodes can affect the network.
- For the node to communicate with one another there is need for all the nodes to be switched on.
- The entire network is affected if one workstation or port goes down.
- The whole network will fail if any one of the cable fails anywhere in the ring.
Hierarchical Network:
This is a specialized kind of bus topology, the terminals are connected in the same fashion as the branches of a tree. It is very easy to extend and if one of the branch fails, it can easily be removed.
Advantages of hierarchical network
- The failure of one segment does not affect the network.
- Easy to extend.
Disadvantages
- It depends heavily on the hub and its failure affects the entire system.
- Maintenance is not easy and cost is high.
EVALUATION:
- What is Network topology?
- List and explain the three types of network topology.
READING ASSIGNMENT
Understanding Data Processing for senior secondary schoolsby Dinehin Victoria pages 280 – 282
ASSIGNMENT
- …………are language that computers used to talk to each other over a network (a) Media (b) user (c) Protocol (d) server
- An example of the bus system is the ………… (a) Ethernet (b) intranet (c) ring (d) star
- ……….. is the term used to describe the physical arrangement of computer in networks. (a) Internet (b) Topology (c) Ethernet (d) hub
- The network configuration in which the terminals are connected in the same fashion as the branches of a tree is called ……… (a) Flat (b) relational (c) Hierarchical (d) network
- In a star ………, a number of small computers are connected to the central resources usually called a host computer or file server (a) Star (b) .Ring (c) Hierachical (d) Flat
See also:
What is a Distributed Database? Definition, Types, and Architecture Explained
Parallel Databases: Architecture, Advantages, and Implementation
Crash Recovery in Databases: Definition, Phases, and ARIES Explained
Samuel Okeke is a highly experienced and skilled Website Developer, Computer Lecturer, IT Instructor, Digital Marketing Expert, Computer Engineer, and Author with over a decade of experience in the educational, digital marketing and IT sectors. He has proven track records of developing and sustaining successful educational projects, including Acadlly, Audio School, and Certifications Exam Prep. He possess a strong passion for education and a commitment to making a positive impact on people and society.