1. Cold storage
The cold storage is a building designed to store certain goods like food stuffs, fruits, vegetables and dairy product within well defined temperature range and relative humidity. The temperature and humidity condition maintained inside a cold storage depend upon the type of product stored inside. Vegetables require the maintenance temperature of around 0°C to 5°C with high RH of 80 to 90%, for milk 4°C to 5°C, -25°C to -30°C for quick freezing of fish. The refrigeration does not improve the quality of food product, it only slow down the deterioration.
Advantages of cold storage
- Substances such as potato, butter can be stored when it is plentifully available and can be supplied when needed.
- Transportation of perishable goods from distant places
- It reduces spoilage of products
It is of two types depending upon the requirement
- Long term ware houses with product in frozen or unfrozen state
- Short term ware houses or retail storage with products usually not frozen Advantages of quick frozen food
- Limits the growth of bacteria
- Reduces the size of the ice crystal formed
- Reduces the separation of water from the cell
It is done by using cold air blast, brine spray or contact evaporators Types of cooling plants for cold storage
- Brine coils placed parallel to and near the centre of ceiling
- Unit condenser with condensing unit outside
- Small ceiling mounted unit.
- Brine coils placed parallel to and near the centre of ceiling: In this arrangement, a central brine pump supplies chilled brine to these coil situated in various rooms of a large cold storage central plant. Thermal air circulation from the coils is No fan is used.
- Unit condenser with condensing unit outside: In this type of cooling plant the cooling coil is placed inside the store and is supplied with direct refrigerant or secondary Room air enters the coil at the bottom, passes over the coils, cools down and that chilled air is blown to the room.
- Small ceiling mounted unit. : These units consist of cooling coil backed by an electric The fan blows the chilled air horizontally or vertically down.
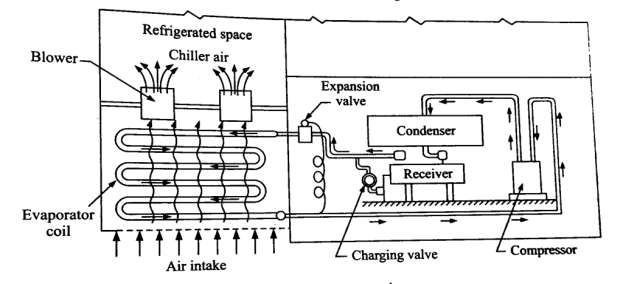
Figure. Cold storage plant
2. Water cooler
The purpose of water cooler is to make water available at a constant temperature irrespective of ambient temperature. Water coolers are used to produce cold water at about 7°C to 13°C. The temperature of cold water is controlled with the help of a thermostat switch set within 7°C to 13°C.
Water cooler may be classified as
- Instantaneous type water cooler: In this type of water cooler, the evaporator consists of two separate cylindrically wound coils made of copper or stainless steel tube, where the cooling coil is wrapped round the pipe line such that by the time water reaches the tank it is cooled to desired temperature. it is subdivided into
- bottle type cooler
- Pressure type cooler
- Self contained or remote type cooler
Storage type water cooler
- Bottle type cooler: In this type, water to be cooled is stored in a bottle or For filling, glass tumblers or faucet are provided. The dripping water from the faucet is collected in the waste water basin. Its usual size is 25 litres and is suitable for places where plumbing installations is expensive and drains are available.
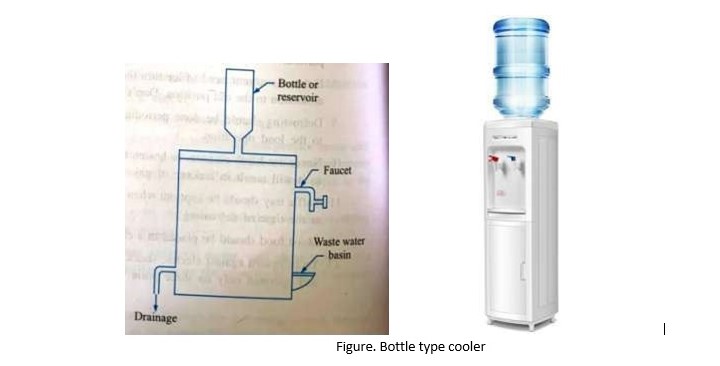
Figure. Bottle type cooler
- Pressure type cooler: In this type of water cooler, the water is supplied under For filling glass tumblers or faucets are provided. The city main water enters the cooler through inlet connection. It then passes through the pre-cooler. The pre cooling is done by the waste water of the cooler. As waste water temperature is low, it is made use of cooling the supply water by passing through a pipe coil wrapped around the drainage line. This arrangement helps to reduce the cooling load for the cooler. The pre cooled water then enters the storage chamber and losses its heat to the refrigerant. The outlet of water pipe is connected at the bottom of the storage tank, which is fitted to a bubbler. Since the water is supplied under pressure the cold water can be obtained from the top mounted at any height of the cooler. The refrigeration system is generally mounted at the bottom of the cooler body and a cooling coil is wrapped around the water tank, where the refrigerants flow. Sometimes a helical or U shape coil is immersed in the water tank. This arrangement gives high heat transfer rate but, it is possible to form undesirable salt due to chemical reaction between water contaminants and copper surface proves to be a great disadvantages.
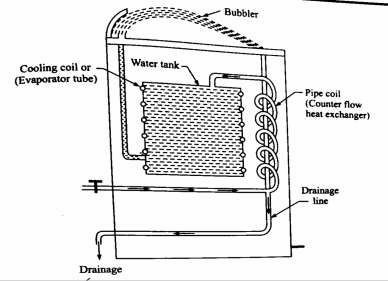

Figure. Pressure type cooler
- Self contained or remote type cooler: This type of cooler employs a mechanical refrigeration The water cooled from the remote cooler is supplied to desired drinking place, away from the system. This type of arrangement does not require extra space near the place of work.
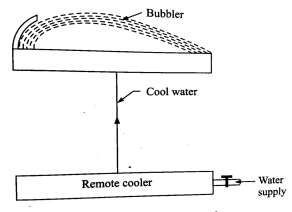
Figure. Remote type cooler
- Storage type water cooler: Such types of coolers are used where continuous supply of water is not Here the water is filled in the storage tank and level of water is kept same by the use of a float valve. The storage tank is surrounded by an evaporator coil through which a low temperature refrigerant flows and takes away the heat and cools the water. When the water is cooled to desired temperature, the thermostat operates and disconnects the power supply to the motor.
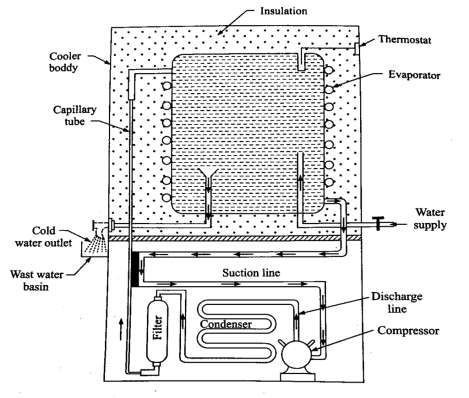
Figure. Storage type water cooler
3. Desert cooler
- Used where humidity is quite low and temperature is
- Uses the principle of evaporative Here the sensible heat is removed and moisture is added to the air.
- Air is allowed to pass through a spray of Water particle takes the heat equivalent to its latent heat and evaporates. The vapour formed is carried away with air. Thus, the air is cooled and humidified.
Main parts
- Blower/fan
- Water circulating pump
- Water wetted pads
- Water tank
- Float valve
The water is filled in the sump of the cooler from water supply mains, the level is controlled by the float valve. A water pump lifts the water and supplies it at the top of the cooler to the water distribution system. The water distribution system consists of small branches of copper pipes which delivers equal amount of water to the troughs and then to the wetted pads. The water which drops back from the pads are collected at the sump and recirculated again. The pump is generally made up of brass, stainless steel or plastic. The blower pulls the air through the wetted pads and delivers it to the space to be cooled. The air which is drawn through the pads is cooled by principle of evaporative cooling.
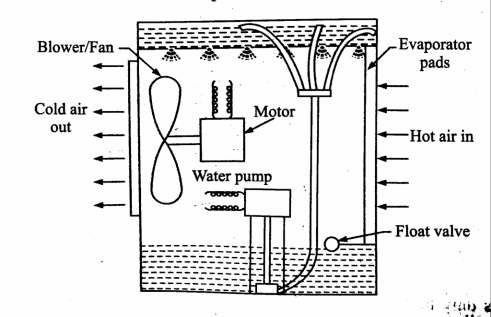
Figure. Desert cooler
4. ICE manufacture
The commercial ice is produced by freezing potable water in standard cans placed in a rectangular tank. The tank is filled with chilled brine. For increasing heat transfer rate from water to chilled brine, the brine solution is kept in constant motion by agitators. The brine temperature is maintained at -10°C to -11°C. Ammonia gas is used as the refrigerant because of its excellent thermal properties. The high pressure and high temperature ammonia vapour enters the condenser, where it is condensed to liquid ammonia by releasing its latent heat. The condensed liquid refrigerant is collected in a receiver and through expansion valve; it is supplied to the evaporator. The expansion valve reduces the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant. When the low pressure and low temperature passes through the evaporator coil surrounding the brine tank, it absorbs the latent heat from the brine solution and gets converted to vapour state. The vapour ammonia is then fed to the compressor where it is compressed and results in consequent increase in temperature and pressure of the vapour refrigerant and the cycle continues.
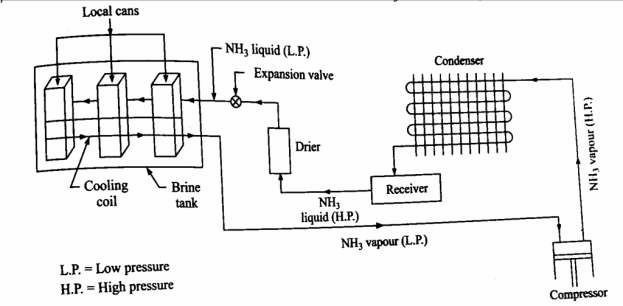
Figure. Ice manufacturing plant
The brine tanks are usually fabricated of 6 mm thick mild steel plate with tie rod welded end to end. The tank is insulated on all four sides and from the bottom. The insulated wooden lids are provided to cover the top to facilitate the removal and replacement of ice cans. The ice cans are fabricated from galvanized steel sheets and are given chromium treatment in order to prevent corrosion. In order to get transparent ice, water in the can is agitated by the use of low pressure air through the tubes suspended from the tops. Due to agitation/stirring, the dissolved impurities are collected at the centre, which should be removed and replaced with fresh water. Brine solutions taken are generally NaCl (sodium chloride) or calcium chloride (CaCl) where as NaCl is mostly preferred because of its low cost. It may be noted that the ice frozen at a temperature lower than -12°C can crack. Therefore, brine temperature is kept at a higher level; say -11°C and -10°C. The rate of freezing decreases as the thickness of the ice layer increases.
5. Domestic refrigerator
It is usually used to preserve foods. The Primary function of refrigerator is to store food at a space maintained at low temperature. Its secondary function is to form the ice cubes for domestic purpose. They are usually specified by internal gross volume and deep freezers volume. A storage temperature of 0-4 °C required for preservation of food. For frozen food, freezers are generally provided at the top or bottom portion of refrigerator space. It may be single door, double door top freezer, double door bottom freezer and side by side door freezer. These refrigerators are divided into two separate compartments, one for fresh foods and other for storage of frozen foods. With double door refrigerators, the freezer space is not subjected to wide temperature variations. This helps in maintaining a stable temperature for preservation of the frozen foods.
The mechanical vapour compression cycle as well as vapour absorption cycle may be adopted for domestic refrigerators and freezers. But, vapour compression cycle is generally preferred because of its compactness and more efficient use of electrical energy. Refrigerant used are generally R-12 or R-
- Compressor is mounted at the bottom. Condenser is mounted at the back side of the refrigerator. Capillary tube is kept in contact with evaporator inlet .Evaporator coil is wrapped around the freezer. The cooling of lower space is done by free convection. The thermostatic sensing element is provided to the evaporator coil which controls the temperature in the freezer. The refrigerator body is provided with good quality insulation in order to prevent heat transfer into the system.
The working of the refrigerator is as follows
- The low pressure and superheated vapour refrigerant is drawn through the suction line to the The accumulator provided between the suction line and the evaporator, collects liquid refrigerant coming out of the evaporator due to incomplete evaporation. The compressor compresses the vapour to high pressure and high temperature. The compressed vapour is then flow through the discharge valve to the condenser.
- In the condenser, the vapour refrigerant at high pressure and high temperature is condensed to liquid
- The high pressure and high temperature liquid refrigerant is then flows through the filter and then enters to the capillary The capillary tube is attached to the cold suction line. The warm refrigerant passing through the capillary tube gives some of its heat to the cold suction line vapour. This increases the heat absorbing quality of the liquid refrigerant and increases the super heat of the vapour entering the compressor. The capillary tube expands the liquid refrigerant at high pressure to the liquid refrigerant at low pressure and low temperature and supplies the required amount to the evaporator.
- In the evaporator, the liquid refrigerant gets evaporated by absorbing heat from the container and from the articles placed in the evaporative chamber and converted to It is then drawn back into the compressor and the cycle repeats.
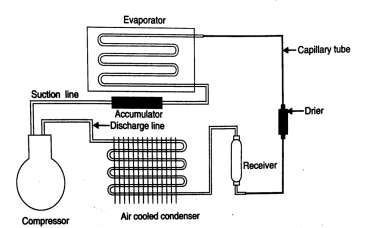
Electrical circuit of a refrigerator
Components
- Starting relay: The starting relay is used to provide necessary starting torque required to start the It disconnects the starting winding of the motor when the motor speed increases.
- Overload protector: The function of the overload protector is to protect the compressor motor winding from damage due to excessive It consists of a bimetallic strip. During normal working of the compressor, the contacts are closed. Whenever there is any abnormal behaviour, the bimetallic strip gets heated and bends and thereby opening the motor contacts and de energising it.
- Thermostat: Thermostat is used to control the temperature in the The bulb of the thermostat is clamped to the evaporator. When the desired temperature obtained, the thermostat bulb senses it, the liquid in it is compresses and operates the bellow of the thermostat and opens the compressor motor contact. When the temperature increases, the liquid in the bulb expands and the below closes the compressor motor contact. It allows the flow of current.
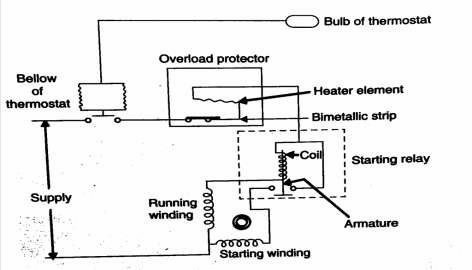
Working:
When electric supply is given to the refrigerator, current passes through the thermostat switch, thermal overload, starting relay coil and then to the main winding of the motor. When the motor is at rest, it draws a very heavy current. When the heavy current flows through the coil of the starting relay, the coil gets energised and it pulls up the armature and closing the starting winding contact. The current flowing through the starting winding provides the starting torque and motor starts. When motor gains normal speed, the current drawn by the main winding of motor become normal. The current in the starting relay is no longer able to hold the relay and it gets released and thereby opening the starting winding contacts. In case starting relay fails to close, the motor will not start. Once it closes and not fails to open, then either thermal overload shall be trip out or fuse shall be blown off.
Defrosting in refrigerator
Since the evaporator in a refrigerator operates at a temperature below 0°C, therefore it is subjected to the accumulation of frost or ice. The frost acts as an insulation that resists the heat transfer to the evaporator and leads to further thickening of the frost. This reduces the evaporator capacity and system efficiency. Thus, the removal of frost at regular interval is necessary.
Methods:
- Manually defrosting by putting off button
- By using push button of defrost thermostat: It is provided at centre of the thermostat It breaks the electrical contact till the evaporator temperature rise and defrosting takes place. This is done till the temperature rises above freezing temperature and defrosting occurs. The refrigerator returns to normal functioning automatically once the defrosting is complete.
Defrost water flows to the condensate pan provided below the evaporator of fresh food compartment. From that place it drains into a tray in the compressor compartment
6. Diary refrigeration:
The milk is known to be one of the perishable foods and if not maintained at sufficient low temperature, it gets spoiled due to bacterial growth. As the temperature of the milk is reduced, the bacterial growth decreases and practically ceases at 0°C to 5°C. But, the bacilli are not killed even at very low temperature. The bacterial content can be eliminated to a great extent by heating the milk to 62°C and holding it at that temperature for about 30 minute. Thereafter to minimize the bacterial growth, the milk is cooled to 4°C to 5°C. This process is called as pasteurization.
In case the heating is done by hot water, it is sprayed around the outside lining of the vat by a distributer, which gets collected in a sump at the bottom of the vat, reheated and sprayed again. In case of steam heating, the steam is allowed to flow in the space provided between lining and the casing of the vat. The heated milk is then cooled, first by cooling tower water and then by the chilled water or brine to 4°C to 5°C. The heating and cooling is done by passing the milk through heat exchanger plates. The milk flows between two plates and the hot water or cooling tower water or chilled brine is circulated through alternate pairs of plates. The direction of flow of heating or cooling fluids is opposite to that of milk to get better heat transfer.
In order to control the fat content of the milk, it is desired to churn the milk. Such milk is known as toned milk. The fat removed is processed as butter and stored at 4°C to 5°C. The cheese from the milk is stored at about 4°C.